Pollination is a crucial process that involves the transfer of pollen grains from the male anther to the female stigma with the aim of producing offspring for the next generation. Insect pollination is an essential element in the functioning of the ecosystem, providing global services of utmost importance. Among insects, bees play a vital role in pollination as they increase the quantity and quality of crop yields. The hair of bees attracts pollen grains through electrostatic forces when they sit on a flower. The stiff hairs on their legs help to clean the pollen and carry it back to their nest. Natural pollinators include bumblebees, orchard bees, squash bees, and solitary bees.
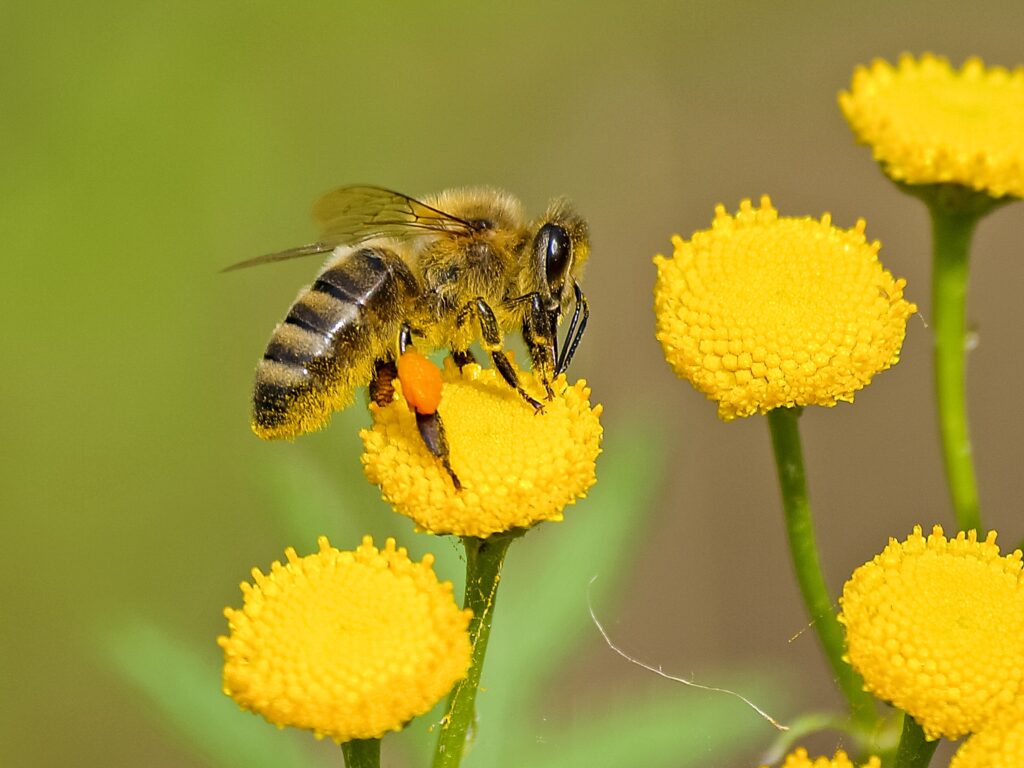

Unfortunately, modern bees are facing numerous threats to their survival, including exposure to pesticides and poor nutrition. As a result, farmers must now buy or rent bee colonies, leading to a rise in food prices. To address this issue, Walmart has filed a patent for a robot bee that could potentially pollinate crops and plants like natural bees. Additionally, other organizations are developing pollinating drones to help offset the decline of bee populations. For example, the patent US20210092920A1 describes a liquid-based method of cross-pollination that delivers pollen to the enclosed stigmas of flowers from recipient plants.
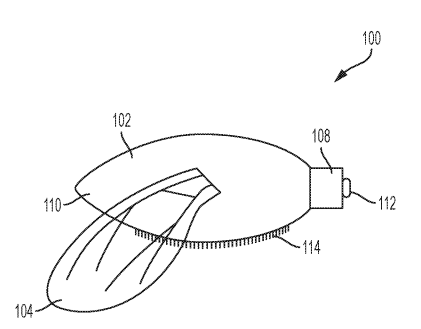
The patent US20190183077A1 titled Autonomous Drone Bees describes a flying device designed in the shape and size of a real bee. This flying device comprises of a body with a head and a pointed tail and two wings attached with one or more sensors.
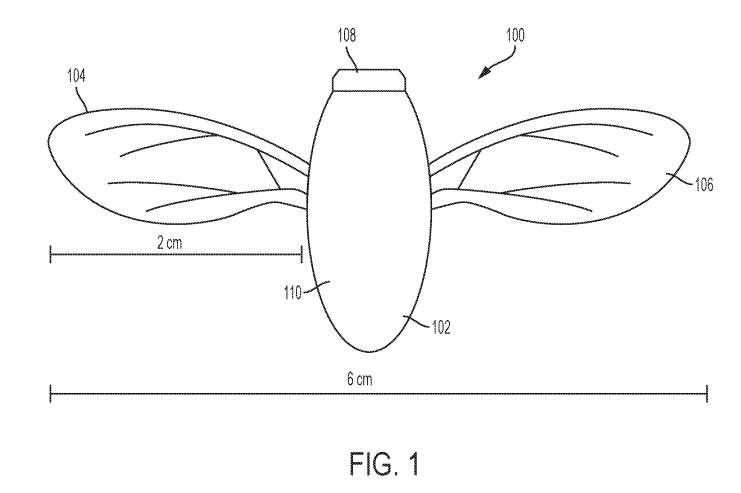
In one of the embodiment of the patent, referring to FIG. 1, an exemplary flying device 100 in the shape of a bee is depicted. The flying device, herein also called drone bee, comprises a body 102 and two wings 104, 106. The body 102 comprises a head 108 and a pointed tail 110. To facilitate flying, the body 102 is hollow and the body casing is made of light material like polycarbonate. The two wings 104, 106 are attached to either side of the body 102. The drone bee is substantially similar to a real bee in shape and size.
These emerging technologies of robotic bees and liquid-based cross-pollination methods have the potential to offset the decline of bee populations and ensure continued pollination of crops and plants, contributing to the functioning of the ecosystem and providing global services of utmost importance.

